Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2012, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (49): 9186-9191.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2012.49.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
In vitro differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into dopaminergic neurons
Wu Xiao-hua1, Chen Nai-yao2
- 1Hongdong Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Hongdong 041600, Shanxi Province, China; 2Affliated Hospital of Hebei United University, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2012-02-19Revised:2012-03-23Online:2012-12-02Published:2013-01-16 -
Contact:Chen Nai-yao, Professor, Attending physician, Affliated Hospital of Hebei United University, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, Chinanychenncmc@yahoo.com.cn E-mail:063000nychenncmc@yahoo.com.cn -
About author:Wu Xiao-hua★, Master, Attending physician, Hongdong Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Hongdong 041600, Shanxi Province, Chinawuxiaohua1124@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Xiao-hua, Chen Nai-yao. In vitro differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into dopaminergic neurons[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(49): 9186-9191.
share this article

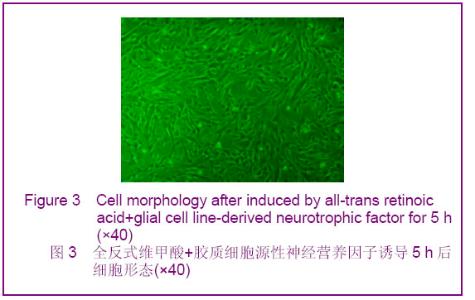
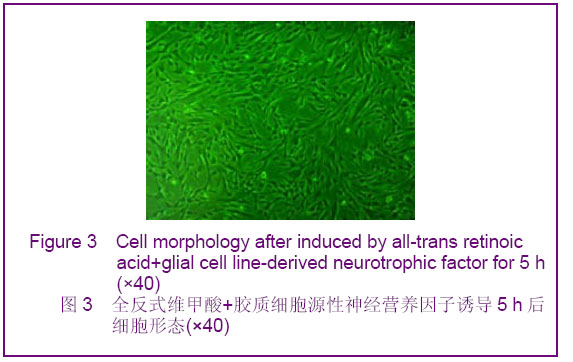
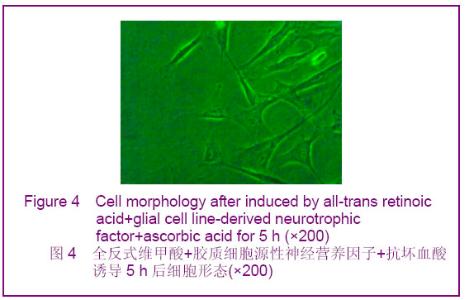
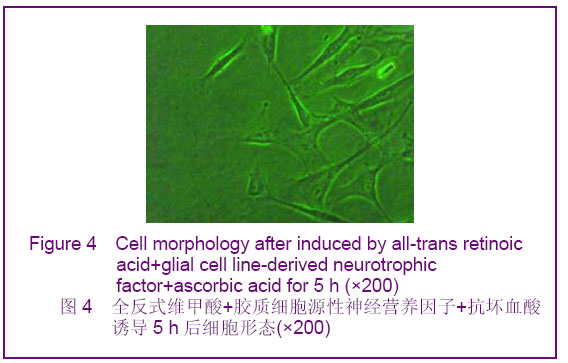
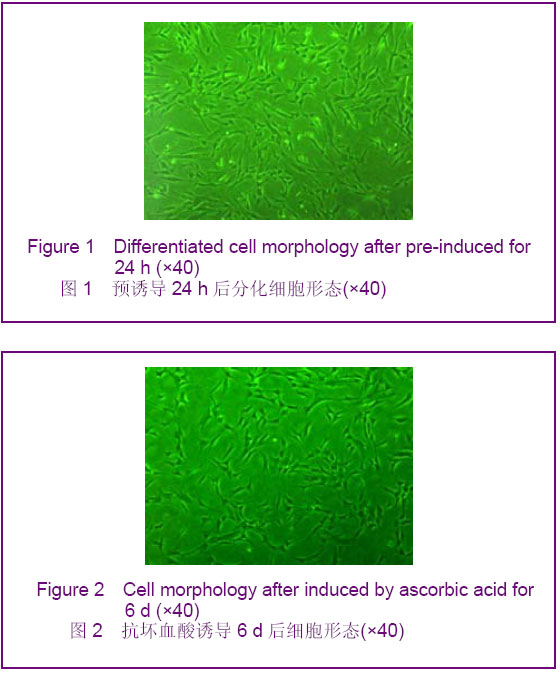
2.1 人脐血间充质干细胞形态观察 人脐血间充质干细胞形态呈均一的长梭形,为成纤维细胞样细胞。待细胞增殖到80%-90%融合时细胞密集生长处呈漩涡状、菊花状。经胰酶消化后的细胞呈圆形,胞体较大,传代后6-12 h,相差显微镜下即可观察到大部分细胞贴壁,于24 h内完全贴壁、伸展,仍呈长梭形。传代后的人脐血间充质干细胞生长迅速,增殖潜伏期较短,为两三天。 2.2 人脐血间充质干细胞诱导分化 经预诱导24 h后,原来梭形的人脐血间充质干细胞体积缩小,立体感增强,边缘变得不规整,极少数细胞有细的指状突起,见图1。未预诱导细胞则仍然维持原来的形态。 对照组:细胞形态基本无变化。 抗坏血酸组:抗坏血酸诱导的间充质干细胞较容易贴壁,分化细胞具有向外迁移速度快、突起长且粗、胞体大且清晰等特性。细胞胞体向内收缩,呈圆形或椭圆形,并向周周长出较长的突起,以后随诱导时间的延长,胞体伸展的突起继续延长,具有神经细胞形态特点的细胞数量逐渐增多,可形成双极或多极细胞,细胞的突起发出分支,相互交织成网,到分化的第4天达到峰值,形态不再发生明显的改变,见图2。"
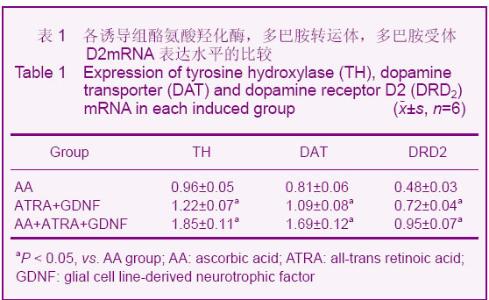
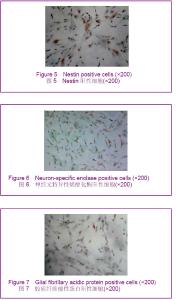
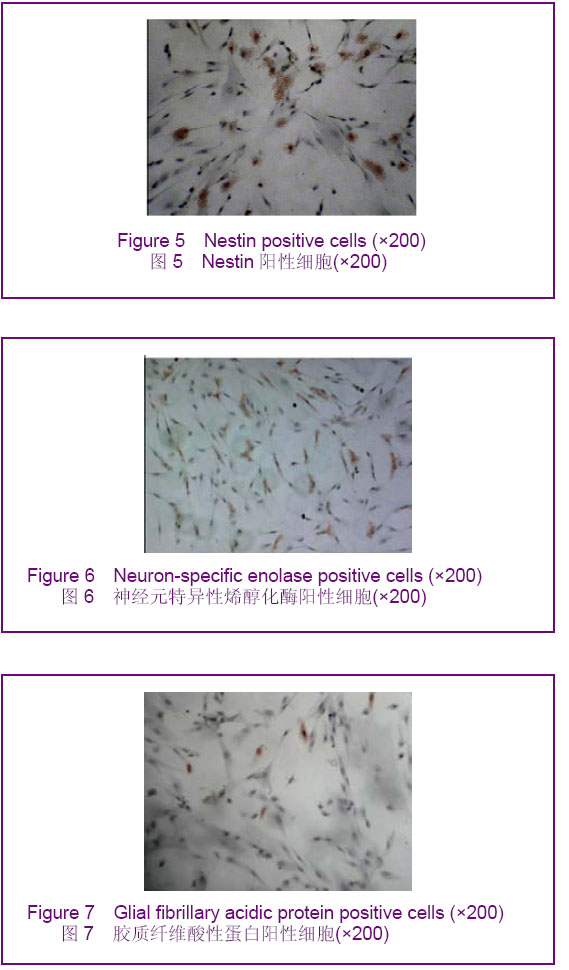
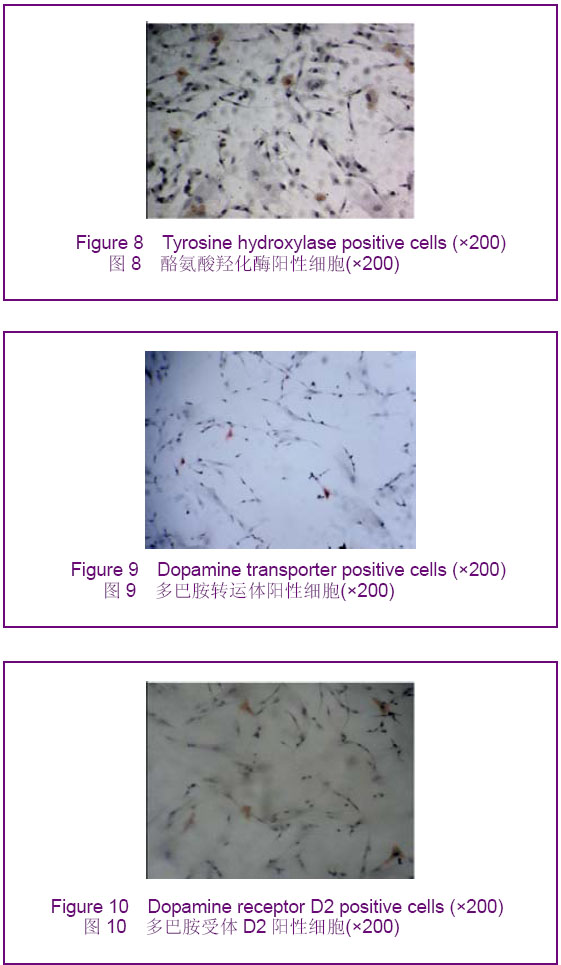
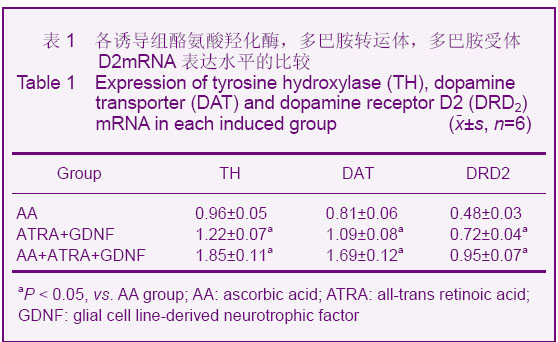
酪氨酸羟化酶阳性细胞率:抗坏血酸,全反式维甲酸 +胶质细胞源性神经营养因子,抗坏血酸+全反式维甲酸+胶质细胞源性神经营养因子各诱导组酪氨酸羟化酶阳性细胞率分别为(7.98±1.59)%,(13.50±1.45)%,(19.17±2.27)%。 多巴胺转运体阳性细胞率:抗坏血酸,全反式维甲酸 +胶质细胞源性神经营养因子,抗坏血酸+全反式维甲酸+胶质细胞源性神经营养因子各诱导组多巴胺转运体阳性细胞率分别为(6.22±1.62)%,(12.07±1.42)%,(17.61±1.45)%。 多巴胺受体D2阳性细胞率:抗坏血酸,全反式维甲酸+胶质细胞源性神经营养因子,抗坏血酸+全反式维甲酸+胶质细胞源性神经营养因子各诱导组多巴胺受体D2阳性细胞率分别为(0.22±0.08)%,(0.39±0.15)%,(0.48± 0.13)%。与对照组比较,各诱导组Nestin、神经元特异性烯醇化酶、胶质纤维酸性蛋白、酪氨酸羟化酶、多巴胺转运体、多巴胺受体D2阳性细胞率均明显升高(P < 0.05)。与抗坏血酸组比较,全反式维甲酸+胶质细胞源性神经营养因子组和抗坏血酸+全反式维甲酸+胶质细胞源性神经营养因子组均明显升高(P < 0.05),且抗坏血酸+全反式维甲酸+胶质细胞源性神经营养因子组升高幅度高于全反式维甲酸+胶质细胞源性神经营养因子组(P < 0.05)。 2.4 Real Time RT-PCR检测结果 与对照组相比,各诱导组中酪氨酸羟化酶mRNA、多巴胺转运体 mRNA、多巴胺受体D2 mRNA的含量均有所增加,其中以抗坏血酸+全反式维甲酸+胶质细胞源性神经营养因子组酪氨酸羟化酶mRNA、多巴胺转运体mRNA、多巴胺受体D2mRNA的含量增加最为明显,全反式维甲酸+胶质细胞源性神经营养因子组次之,抗坏血酸组单独诱导较弱,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表1。"
| [1] Goodwin HS, Bicknese AR, Chien SN,et al. Multilineage differentiation activity by cells isolated from umbilical cord blood: expression of bone, fat, and neural markers. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2001;7(11):581-588.[2] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ,et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons.J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.[3] Chiou SH, Kao CL, Peng CH,et al. A novel in vitro retinal differentiation model by co-culturing adult human bone marrow stem cells with retinal pigmented epithelium cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;326(3):578-585.[4] Li RP,Ji FQ,Sun HM,et al.Jiepou Xuebao. 2007;38(2):148-152.李荣平,季凤清,孙海梅,等.人脐血干细胞定向分化为多巴胺能神经元的实验研究[J].解剖学报,2007,38(2):148-152.[5] Wu XM,Ding WR,Wang WZ,et al. Linchuang Shenjingbingxue Zazhi. 2007;20(2):112-114.吴晓牧,丁伟荣,王卫真,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞向多巴胺能神经元分化的体外研究[J].临床神经病学杂志,2007,20(2):112-114.[6] Bagga V, Dunnett SB, Fricker-Gates RA. Ascorbic acid increases the number of dopamine neurons in vitro and in transplants to the 6-OHDA-lesioned rat brain. Cell Transplant. 2008;17(7):763-773.[7] Choong PF, Mok PL, Cheong SK,et al. Generating neuron-like cells from BM-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Cytotherapy. 2007;9(2):170-183.[8] Yu DH, Lee KH, Lee JY,et al. Changes of gene expression profiles during neuronal differentiation of central nervous system precursors treated with ascorbic acid. J Neurosci Res. 2004;78(1):29-37.[9] Lee HY, Naha N, Ullah N,et al. Effect of the co-administration of vitamin C and vitamin E on tyrosine hydroxylase and Nurr1 expression in the prenatal rat ventral mesencephalon. J Vet Med Sci. 2008;70(8):791-797. [10] Agrawal AK, Chaturvedi RK, Shukla S,et al. Restorative potential of dopaminergic grafts in presence of antioxidants in rat model of Parkinson's disease. J Chem Neuroanat. 2004; 28(4):253-264.[11] Guan K, Chang H, Rolletschek A,et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived neurogenesis. Retinoic acid induction and lineage selection of neuronal cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2001; 305(2):171-176.[12] Akerud P, Alberch J, Eketjäll S,et al. Differential effects of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and neurturin on developing and adult substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. J Neurochem. 1999;73(1):70-78.[13] Lin LF, Doherty DH, Lile JD,et al. GDNF: a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons.Science. 1993;260(5111):1130-1132.[14] Yasuhara T, Shingo T, Date I. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) therapy for Parkinson's disease. Acta Med Okayama. 2007;61(2):51-56.[15] Ledda F, Paratcha G, Sandoval-Guzmán T, et al. GDNF and GFRalpha1 promote formation of neuronal synapses by ligand-induced cell adhesion. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10(3):293- 300.[16] Kong X, Li X, Cai Z,et al. Melatonin regulates the viability and differentiation of rat midbrain neural stem cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2008;28(4):569-579.[17] Smith MP, Cass WA. GDNF reduces oxidative stress in a 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 2007;412(3):259-263.[18] Chu TH, Li SY, Guo A,et al. Implantation of neurotrophic factor-treated sensory nerve graft enhances survival and axonal regeneration of motoneurons after spinal root avulsion. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009;68(1):94-101. |
| [1] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [2] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Liu Xun, Ouyang Hougan, Pan Rongbin, Wang Zi, Yang Fen, Tian Jiaxuan . Optimal parameters for physical interventions in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6727-6732. |
| [4] | Hu Enxi, He Wenying, Tao Xiang, Du Peijing, Wang Libin. Regulation of THZ1, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 7, on stemness of glioma stem cells and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5374-5381. |
| [5] | Lin Meiyu, Zhao Xilong, Gao Jing, Zhao Jing, Ruan Guangping. Action mechanism and progress of stem cells against ovarian granulosa cell senescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5414-5421. |
| [6] | Tian Zhenli, Zhang Xiaoxu, Fang Xingyan, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on lipid metabolism in human hepatocytes and regulatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4956-4964. |
| [7] | Han Fang, Shu Qing, Jia Shaohui, Tian Jun. Electrotactic migration and mechanisms of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4984-4992. |
| [8] | Hu Chen, Jiang Ying, Chen Jia, Qiao Guangwei, Dong Wen, Ma Jian. Preparation and characterization of alendronate/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel films [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4720-4730. |
| [9] | Yang Chao, Luo Zongping. Small molecule drug TD-198946 enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2648-2654. |
| [10] | Li Xiaofeng, Zhao Duo, Ouyang Qin, Pang Zixiang, Li Yuquan, Chen Qianfen. Protective effect of mangiferin on oxidative stress injury in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2669-2674. |
| [11] | Hu Zezun, Yang Fanlei, Xu Hao, Luo Zongping. Effect of surface roughness of polydimethylsiloxane on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under stretching conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1981-1989. |
| [12] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [13] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [14] | Liu Haowen, Qiao Weiping, Meng Zhicheng, Li Kaijie, Han Xuan, Shi Pengbo. Regulation of osteogenic effects by bone morphogenetic protein/Wnt signaling pathway: revealing molecular mechanisms of bone formation and remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 563-571. |
| [15] | Zhou Shijie, Li Muzhe, Yun Li, Zhang Tianchi, Niu Yuanyuan, Zhu Yihua, Zhou Qinfeng, Guo Yang, Ma Yong, Wang Lining. Effect of Wenshen Tongluo Zhitong formula on mouse H-type bone microvascular endothelial cell/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 8-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||